Budgeting & Scaling Plan
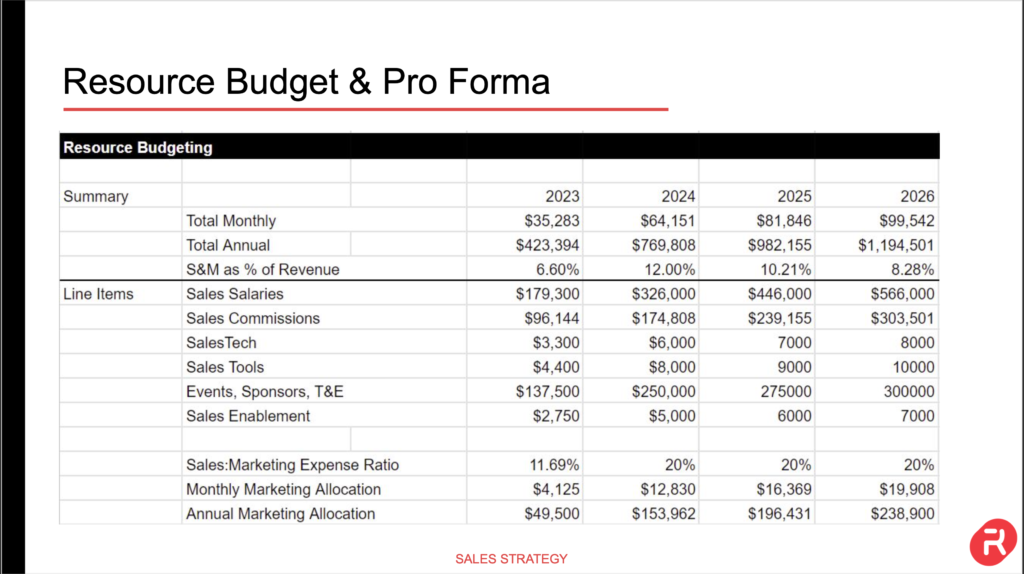
Overview & Revenue Projections
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend to repeat predefined chunks as necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It uses a dictionary of over 200 Latin words, combined with a handful of model sentence structures, to generate Lorem Ipsum which looks reasonable. The generated Lorem Ipsum is therefore always free from repetition, injected humour, or non-characteristic words etc.
Budget Allocations
Personnel Costs:
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend to repeat predefined chunks as necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet.
Marketing & Sales Tools:
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend to repeat predefined chunks as necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet.
Operational Expenses:
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend to repeat predefined chunks as necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet.
Scalability Planning
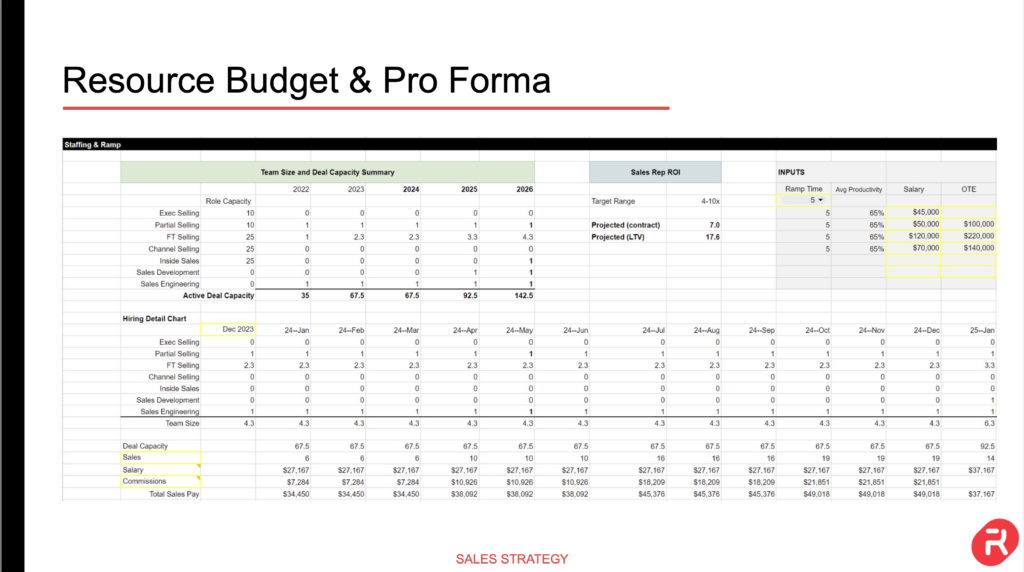
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend to repeat predefined chunks as necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It uses a dictionary of over 200 Latin words, combined with a handful of model sentence structures, to generate Lorem Ipsum which looks reasonable. The generated Lorem Ipsum is therefore always free from repetition, injected humour, or non-characteristic words etc.
- Budget for scaling the sales team
- Investment in scalable infrastructure
- Costs associated with entering new markets
- Flexibility for unexpected growth opportunities
Performance Metrics and KPIs
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend to repeat predefined chunks as necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It uses a dictionary of over 200 Latin words, combined with a handful of model sentence structures, to generate Lorem Ipsum which looks reasonable. The generated Lorem Ipsum is therefore always free from repetition, injected humour, or non-characteristic words etc.
- Budget for performance tracking tools
- Cost of sales analytics platforms
- Investment in data quality and management
- External benchmarking and market research
Customer Success and Retention
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend to repeat predefined chunks as necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It uses a dictionary of over 200 Latin words, combined with a handful of model sentence structures, to generate Lorem Ipsum which looks reasonable. The generated Lorem Ipsum is therefore always free from repetition, injected humour, or non-characteristic words etc.
- Customer success software and tools
- Support team salaries and benefits
- Training programs for customer success teams
- Customer feedback and survey tools
Sales Process Optimization
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend to repeat predefined chunks as necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It uses a dictionary of over 200 Latin words, combined with a handful of model sentence structures, to generate Lorem Ipsum which looks reasonable. The generated Lorem Ipsum is therefore always free from repetition, injected humour, or non-characteristic words etc.
- Sales process auditing and consulting
- Implementation of new sales methodologies
- Continuous improvement initiatives
- Automation of repetitive tasks
Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC)
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend to repeat predefined chunks as necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It uses a dictionary of over 200 Latin words, combined with a handful of model sentence structures, to generate Lorem Ipsum which looks reasonable. The generated Lorem Ipsum is therefore always free from repetition, injected humour, or non-characteristic words etc.
- Advertising spend
- Sales promotions and discounts
- Partnership and affiliate marketing costs
- Customer onboarding costs
Marketing and Lead Generation
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend to repeat predefined chunks as necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It uses a dictionary of over 200 Latin words, combined with a handful of model sentence structures, to generate Lorem Ipsum which looks reasonable. The generated Lorem Ipsum is therefore always free from repetition, injected humour, or non-characteristic words etc.
- Content creation (blogs, whitepapers, videos)
- Digital marketing (SEO, PPC, social media)
- Email marketing campaigns
- Event marketing (trade shows, webinars, conferences)
Sales Tools and Technology
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend to repeat predefined chunks as necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It uses a dictionary of over 200 Latin words, combined with a handful of model sentence structures, to generate Lorem Ipsum which looks reasonable. The generated Lorem Ipsum is therefore always free from repetition, injected humour, or non-characteristic words etc.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software
- Sales enablement tools (content management, email tracking)
- Analytics and reporting tools
- Communication tools (video conferencing, collaboration platforms)
Recruitment and Training
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend to repeat predefined chunks as necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It uses a dictionary of over 200 Latin words, combined with a handful of model sentence structures, to generate Lorem Ipsum which looks reasonable. The generated Lorem Ipsum is therefore always free from repetition, injected humour, or non-characteristic words etc.
- Hiring costs (recruitment agencies, job postings)
- Onboarding programs
- Continuous training and development
- Certifications and professional development courses
Sales Team Compensation
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend to repeat predefined chunks as necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It uses a dictionary of over 200 Latin words, combined with a handful of model sentence structures, to generate Lorem Ipsum which looks reasonable. The generated Lorem Ipsum is therefore always free from repetition, injected humour, or non-characteristic words etc.
- Base salaries
- Commissions and bonuses
- Incentive programs
- Benefits and perks
When developing a new sales operation budget and scaling plan, a software company should consider several key factors to ensure a comprehensive, realistic, and strategic approach. Here are the main considerations:
1. Market Analysis
- Target Market Identification: Clearly define the target market segments, including geographic regions, industries, and customer profiles.
- Competitive Landscape: Analyze competitors to understand their strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning.
2. Revenue Projections
- Sales Forecasting: Develop detailed sales forecasts based on historical data, market trends, and potential new customer acquisition.
- Pricing Strategy: Determine optimal pricing models, including subscription plans, one-time fees, and any discounts or promotions.
3. Budget Allocation
- Personnel Costs: Budget for hiring and training sales staff, including salaries, commissions, and benefits.
- Marketing and Sales Tools: Allocate funds for CRM systems, marketing automation tools, and other sales enablement technologies.
- Operational Expenses: Include travel expenses, office space, and other overhead costs associated with scaling the sales operation.
4. Sales Strategy
- Sales Channels: Decide on the sales channels to be used, such as direct sales, online sales, partnerships, or resellers.
- Customer Acquisition Strategies: Plan for lead generation activities, including digital marketing, trade shows, and networking events.
5. Performance Metrics
- KPIs and Metrics: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) such as customer acquisition cost (CAC), lifetime value (LTV), and sales cycle length.
- Data Analytics: Use data analytics to track sales performance, customer engagement, and campaign effectiveness.
6. Scalability
- Process Automation: Implement automated processes to handle increasing sales volumes without proportional increases in headcount.
- Infrastructure Readiness: Ensure that IT infrastructure can support growth, including cloud services, customer support, and data security measures.
7. Risk Management
- Financial Risks: Identify financial risks such as cash flow issues and budget overruns, and plan for contingencies.
- Market Risks: Consider potential market changes, such as economic downturns or new competitors, and develop strategies to mitigate these risks.
8. Team Structure
- Organizational Design: Plan the structure of the sales team, including roles and responsibilities, to ensure effective coverage and management.
- Talent Acquisition: Develop a recruitment plan to attract and retain top sales talent.
9. Training and Development
- Sales Training Programs: Invest in continuous training programs to enhance the skills and knowledge of the sales team.
- Onboarding Processes: Create effective onboarding processes for new hires to ensure they are quickly productive.
10. Customer Retention
- Customer Success Initiatives: Implement customer success strategies to enhance satisfaction, reduce churn, and increase upsell opportunities.
- Feedback Loops: Establish mechanisms for collecting and acting on customer feedback to continuously improve the product and sales approach.
11. Legal and Compliance
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that sales practices comply with all relevant laws and regulations, including data protection and anti-fraud measures.
- Contracts and Agreements: Develop standard contracts and service agreements that protect the company and its customers.
By considering these factors, a software company can create a robust sales operation budget and scaling plan that supports sustainable growth and competitive advantage. Regular reviews and adjustments to the plan will also be necessary to adapt to changing market conditions and business objectives.
ChatGPT can make mistakes. Check important info.
When developing a new sales operation budget and scaling plan, a software company should consider several key factors to ensure a comprehensive, realistic, and strategic approach. Here are the main considerations:
1. Market Analysis
- Target Market Identification: Clearly define the target market segments, including geographic regions, industries, and customer profiles.
- Competitive Landscape: Analyze competitors to understand their strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning.
2. Revenue Projections
- Sales Forecasting: Develop detailed sales forecasts based on historical data, market trends, and potential new customer acquisition.
- Pricing Strategy: Determine optimal pricing models, including subscription plans, one-time fees, and any discounts or promotions.
3. Budget Allocation
- Personnel Costs: Budget for hiring and training sales staff, including salaries, commissions, and benefits.
- Marketing and Sales Tools: Allocate funds for CRM systems, marketing automation tools, and other sales enablement technologies.
- Operational Expenses: Include travel expenses, office space, and other overhead costs associated with scaling the sales operation.
4. Sales Strategy
- Sales Channels: Decide on the sales channels to be used, such as direct sales, online sales, partnerships, or resellers.
- Customer Acquisition Strategies: Plan for lead generation activities, including digital marketing, trade shows, and networking events.
5. Performance Metrics
- KPIs and Metrics: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) such as customer acquisition cost (CAC), lifetime value (LTV), and sales cycle length.
- Data Analytics: Use data analytics to track sales performance, customer engagement, and campaign effectiveness.
6. Scalability
- Process Automation: Implement automated processes to handle increasing sales volumes without proportional increases in headcount.
- Infrastructure Readiness: Ensure that IT infrastructure can support growth, including cloud services, customer support, and data security measures.
7. Risk Management
- Financial Risks: Identify financial risks such as cash flow issues and budget overruns, and plan for contingencies.
- Market Risks: Consider potential market changes, such as economic downturns or new competitors, and develop strategies to mitigate these risks.
8. Team Structure
- Organizational Design: Plan the structure of the sales team, including roles and responsibilities, to ensure effective coverage and management.
- Talent Acquisition: Develop a recruitment plan to attract and retain top sales talent.
9. Training and Development
- Sales Training Programs: Invest in continuous training programs to enhance the skills and knowledge of the sales team.
- Onboarding Processes: Create effective onboarding processes for new hires to ensure they are quickly productive.
10. Customer Retention
- Customer Success Initiatives: Implement customer success strategies to enhance satisfaction, reduce churn, and increase upsell opportunities.
- Feedback Loops: Establish mechanisms for collecting and acting on customer feedback to continuously improve the product and sales approach.
11. Legal and Compliance
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that sales practices comply with all relevant laws and regulations, including data protection and anti-fraud measures.
- Contracts and Agreements: Develop standard contracts and service agreements that protect the company and its customers.
By considering these factors, a software company can create a robust sales operation budget and scaling plan that supports sustainable growth and competitive advantage. Regular reviews and adjustments to the plan will also be necessary to adapt to changing market conditions and business objectives.